 Over 1 Billion Smartphones and according to google analytics in 2017 there were 178.1 billion, in 2018 205.4 billion and expected to be 258.2 Billion application downloads in 2022. Mobile development is positively one of the original and actively increasing segments. The mobile application market is perhaps dominated by Google apps (Gmail, Maps, and Search), Social media (Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, YouTube) and Gaming apps (Angry Birds, Temple Run). Titans like Amazon, MacDonald’s, and ZARA are using mobile applications for branding, refining customer engagement, direct marketing etc. Small and midsize industries are also following the mobile trend. Eventually an effective mobile strategy involves more than just a mobile-friendly website. Mobile application growth is driven by developments in technology which involves businesses to have a vision for the next few decades. To illustrate more of the trends which will govern the future of mobile application development are below:
Over 1 Billion Smartphones and according to google analytics in 2017 there were 178.1 billion, in 2018 205.4 billion and expected to be 258.2 Billion application downloads in 2022. Mobile development is positively one of the original and actively increasing segments. The mobile application market is perhaps dominated by Google apps (Gmail, Maps, and Search), Social media (Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, YouTube) and Gaming apps (Angry Birds, Temple Run). Titans like Amazon, MacDonald’s, and ZARA are using mobile applications for branding, refining customer engagement, direct marketing etc. Small and midsize industries are also following the mobile trend. Eventually an effective mobile strategy involves more than just a mobile-friendly website. Mobile application growth is driven by developments in technology which involves businesses to have a vision for the next few decades. To illustrate more of the trends which will govern the future of mobile application development are below:
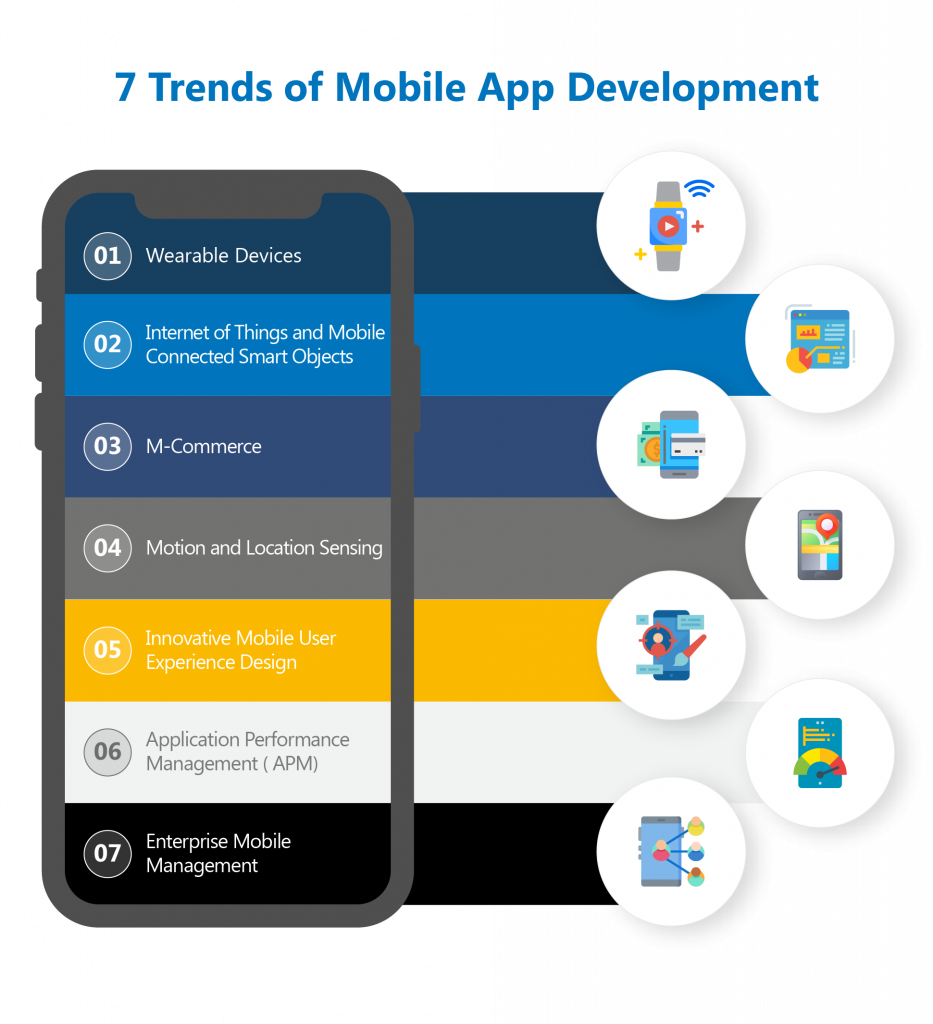
#1 Wearable Devices
According to IDC, 101.9 million wearable devices were shipped in 2016, up by a strong 29 percent from the 79 million units shipped in 2015. Smart wearable like the Apple Watch and Microsoft’s Hololens indications an approaching change in computing and the evolution from basic to smart wearable. This unlocks new chances for sellers, app developers, and accessory makers. The smartphone will become the center of a personal-area system containing of wearable gadgets such as on-body healthcare sensors, smart jewelry, smart watches, display devices (like Google Glass. These gadgets will connect with mobile applications to send information in new ways. And will permit a wide variety of products and services in areas such as sport, fitness, fashion, hobbies and healthcare. Therefore, wearable devices linked with smartphones will influence the next generation of mobile application development strategies.
#2 Internet of Things and Mobile-connected Smart Objects
Gartner says there will be 26 billion connected devices by 2020 which includes several hundred smart items such as LED light bulbs, toys, domestic appliances, sports equipment, medical devices and controllable power sockets etc. These home smart objects will be a part of the Internet of Things and will communicate through an App on a smartphone or tablet. Smartphones will act as remote controls, demonstrating and examining information, interfacing with social networks to monitor “things” that can pay for subscription services, order spare consumables and updating object firmware.
Google has two projects Nest and Brillo specifically targeting IoT. Nest develops home automation products- smoke alarm, camera, and thermostat, whereas Brillo is an IoT operating system which supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy, and other Android belongings. Apple recently launched some products of ‘Home-kit’ that will permit you to have wireless and electrical control of your household uses. The products include light dimmers, air monitors, a thermostat, and an entire smart home hub which can be controlled through apps and Siri, allowing homes to be automated by voice command. On the similar lines, Amazon launched ‘Amazon Echo’ which is a voice command device for answering questions, playing music and controlling smart devices.
#3 M-Commerce
As a broad definition M-commerce (mobile commerce) is the buying and selling of goods and services through wireless handheld devices such as smartphones and tablets. We at BC believe positive trend in mobile purchases will remain over the next 4 years as more and more consumers adapt to m-commerce. Increasing popularity of Apple Pay and Google Wallet will simplify purchases using the mobile phones instead of debit or credit cards. This will require developers to build a mobile application that can practice transactions without the need of physical debit/credit cards or cash. Coupled with wearable that can process payments m-commerce will take a changed shape. Beyond data collection and projecting analytics, wearable will also show a crucial role in the upcoming of mobile payments and customer loyalty.
#4 Motion and Location Sensing
Most smart phones have location sensor competencies which use numerous placing methods to provide different location data. Knowing an individual’s location to within a few meters is useful for providing extremely relevant background information and services. Motion sensing apps are used in security, anti-theft, power-saving and games. Location sensing is useful in Geo-tagging, Games, Vehicle navigation, and fitness apps. Apps abusing detailed indoor location currently use technologies such as Wi-Fi, imaging , and geomagnetic. On the longer run technologies such as smart lighting will also become important. Precise indoor location sensing, combined with mobile applications, will allow a new generation of enormously personalized services and information.
#5 Innovative Mobile User Experience Design
Actual display of data and content on your mobile user interface is important for a sound user experience. Successful mobile application companies, such as Instagram, Pinterest, and Wunderlist, have developed new patterns showing spontaneous designs and interactive interfaces. Designers are also creating apps that can accommodate mobile tests, such as partial user attention and interruption. Apps should exploit technologies with novel features such as collaborating content layers, circular design pattern, cards and manipulation of content. These features create an “augmented reality” by allowing the users to interact with the content in further detail. Leading consumer apps are setting high standards for user interface design, and all organizations must master new skills and work with new partners to meet growing user expectations.
#6 Application Performance Management (APM)
There are two influences which are key to performance blockages in app testing i.e. variety of mobile devices and the non-deterministic nature of mobile networks. But mobile metrics and monitoring tools cooperatively known as Application Performance Management (APM) has enhanced the testing and quality assurance. APM provides visibility into app behavior, delivers statistics about which devices and OSs are accepted, and monitors user behavior to determine which app features are being successfully abused. With the application setting and enterprise infrastructures shifting to the cloud, APM tools face increased issues to provide real performance benefits across systems with virtual boundaries. Modern enterprises require robust tools that can monitor resources used by applications, correlate that data with meaningful user insights, and align performance with business processes.
#7 Enterprise mobile management
Enterprise mobile management (EMM) is a set of people, processes, and technology using mobile computing for streamlining businesses. The main dimensions of EMM are security, application management, and financial management. It also includes mobile device management, mobile application management, application wrapping and containerization, and some elements of enterprise file management and sharing. Such tools will mature, grow in scope and eventually address a wide range of mobile management needs across all popular Operating Systems on smartphones, tablets, and PCs. Thus, EMM represents the future evolution and convergence of several mobile management, security, and support technologies.
We cannot deny that mobile applications have become an integral element of the digital ecos ystem. The skills required in building consumer apps are in greater demand than ever now compelling businesses to take mobility seriously. Businesses should keep an eye on these trends to align their mobile application development strategies.